DANGER-WORD-OF-DOUBLESPEAK (INCLUDE) Hocus-Pocus
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Za1cyx0FGeQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sjWyHS3tAFQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z0DC05zpzdI
The term "doublespeak" derives from two concepts in George Orwell's novel Nineteen Eighty-Four, "doublethink" and "Newspeak", though the term is not used in the book. Another variant, "doubletalk", also referring to deliberately ambiguous speech, did exist at the time Orwell wrote his book, but the usage of "doublespeak", as well as of "doubletalk", in the sense emphasizing ambiguity clearly postdates the publication of Nineteen Eighty-Four. Parallels have also been drawn between doublespeak and Orwell's classic essay Politics and the English Language, which discusses the distortion of language for political purposes. In it he observes that political language serves to distort and obfuscate reality. Orwell's description of political speech is extremely similar to the contemporary definition of doublespeak:
In our time, political speech and writing are largely the defence of the indefensible… Thus political language has to consist largely of euphemism, question-begging and sheer cloudy vagueness… the great enemy of clear language is insincerity. Where there is a gap between one's real and one's declared aims, one turns as it were instinctively to long words and exhausted idioms…
The writer Edward S. Herman cited what he saw as examples of doublespeak and doublethink in modern society.[9] Herman describes in his book Beyond Hypocrisy the principal characteristics of doublespeak:
What is really important in the world of doublespeak is the ability to lie, whether knowingly or unconsciously, and to get away with it; and the ability to use lies and choose and shape facts selectively, blocking out those that don’t fit an agenda or program.[10]
Edward S. Herman and Noam Chomsky comment in their book Manufacturing Consent: the Political Economy of the Mass Media that Orwellian doublespeak is an important component of the manipulation of the English language in American media, through a process called dichotomization, a component of media propaganda involving "deeply embedded double standards in the reporting of news." For example, the use of state funds by the poor and financially needy is commonly referred to as "social welfare" or "handouts," which the "coddled" poor "take advantage of." These terms, however, are not as often applied to other beneficiaries of government spending such as military spending.[11] The bellicose language used interchangeably with calls for peace towards Armenia by Azerbaijani president Aliyev after the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War were described as doublespeak in media.[12]
Advertisers can use doublespeak to mask their commercial intent from users, as users' defenses against advertising become more entrenched.[13] Some are attempting to counter this technique with a number of systems offering diverse views and information to highlight the manipulative and dishonest methods that advertisers employ.[14]
According to Jacques Ellul, "the aim is not to even modify people’s ideas on a given subject, rather, it is to achieve conformity in the way that people act." He demonstrates this view by offering an example from drug advertising. Use of doublespeak in advertisements resulted in aspirin production rates rising by almost 50 percent from over 23 million pounds in 1960 to over 35 million pounds in 1970.
Doublespeak, particularly when exaggerated, can be used as a device in satirical comedy and social commentary to ironically parody political or bureaucratic establishments' intent on obfuscation or prevarication. The television series Yes Minister is notable for its use of this device.[16] Oscar Wilde was an early proponent of this device and a significant influence on Orwell.
William D. Lutz, professor emeritus at Rutgers University-Camden has served as the third chairman of the Doublespeak Committee since 1975. In 1989, both his own book Doublespeak and, under his editorship, the committee's third book, Beyond Nineteen Eighty-Four, were published. Beyond Nineteen Eighty-Four consists of 220 pages and eighteen articles contributed by long-time Committee members and others whose bodies of work have contributed to public understanding about language, as well as a bibliography of 103 sources on doublespeak.[20] Lutz was also the former editor of the now defunct Quarterly Review of Doublespeak, which examined the use of vocabulary by public officials to obscure the underlying meaning of what they tell the public. Lutz is one of the main contributors to the committee as well as promoting the term "doublespeak" to a mass audience to inform them of its deceptive qualities.




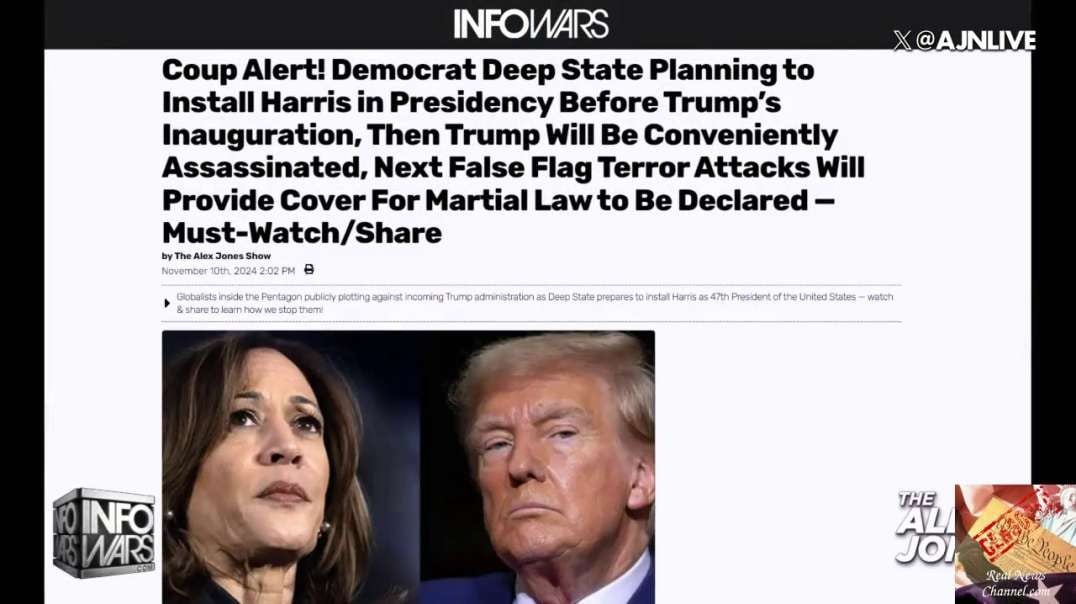



![Kim Clement PROPHETIC WORD🚨 [KIM SAW: TRUMP CALLED BACK TO THE WHITE HOUSE 2024] Two Terms Prophecy](https://video.ugetube.com/thumb/8_SSS_OOZzA_HleLPxYh2naRyPu.jpg)
![Kim Clement PROPHETIC WORD🚨 [KIM SAW: OF GODS PLAN FOR TRUMP] Powerful Prophecy](https://video.ugetube.com/thumb/fDwJbfoeNv4_FySRIPoy9gjVOKv.jpg)
![Kim Clement PROPHETIC WORD🚨[WARNING: FOR NOVEMBER] END OF 2024-KIM SAW THE NEXT PRESIDENT Prophecy](https://video.ugetube.com/thumb/DMFk60N4eaQ_NrPS5cGTWQhoZjt.jpg)